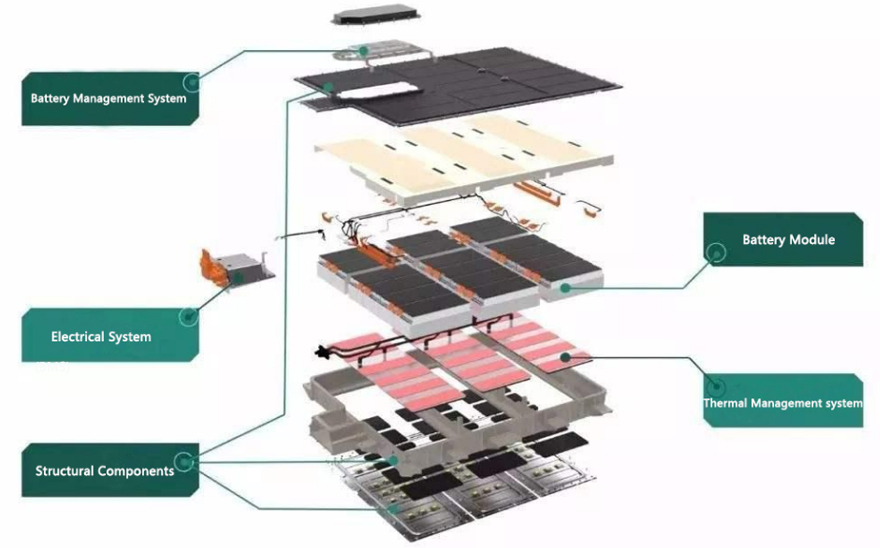
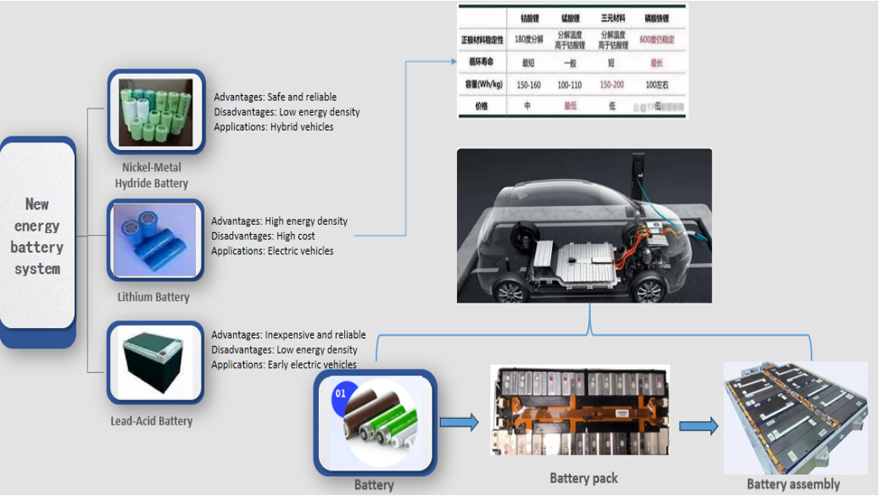
Power batteries serve as the engine equivalent for gasoline vehicles and the primary power source for new energy vehicles. Power battery modules are assembled by “packaging” individual cells. Power batteries are primarily categorized into battery packs, modules, and cells.
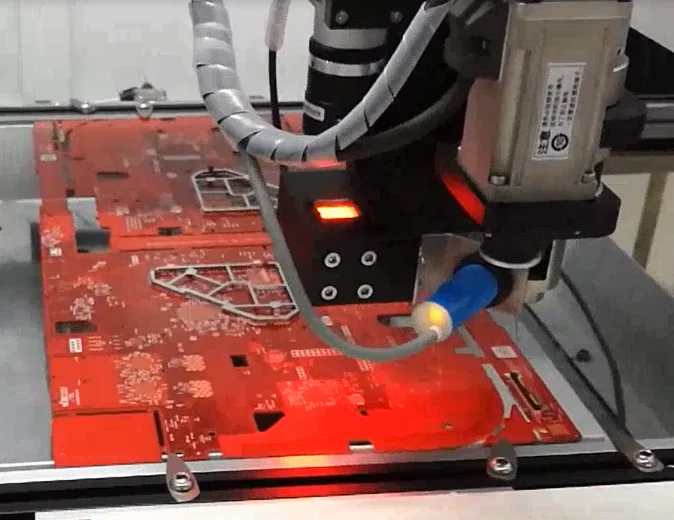
Within the power battery sector, dispensing machines play a crucial role in cell encapsulation and battery pack assembly processes.
 1.Battery Packs
1.Battery Packs
Battery packs typically consist of battery modules, thermal management systems, battery management systems (BMS), electrical systems, and structural components.

2.Battery Modules
These are products formed by combining lithium-ion cells through series and parallel connections, then integrating individual cell monitoring and management devices.
3.Battery Cell
Composed of a cathode, anode, separator, and electrolyte. Its primary operating principle relies on lithium-ion migration between the cathode and anode to achieve charging and discharging.
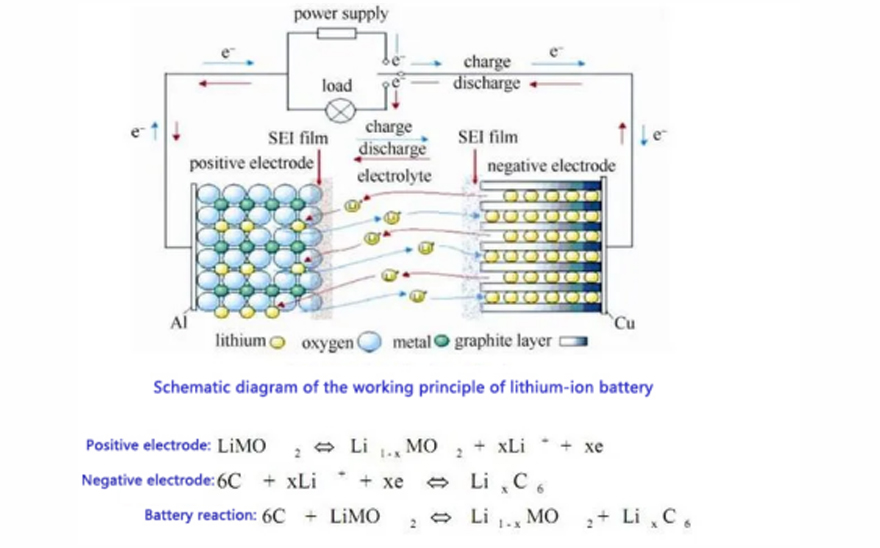
Power batteries can be classified by manufacturing materials into lead-acid power batteries, nickel-metal hydride power batteries, and lithium-ion power batteries. Additionally, power batteries include fuel cells. Currently, lithium iron phosphate power batteries and ternary lithium power batteries are widely used in new energy electric vehicles.
Application of dispensing &potting machines in power batteries
a.Battery cell bonding and encapsulation
Power batteries operate in demanding environments where high temperatures, vibrations, and compression impose stringent requirements on cell encapsulation:
High reliability: Cells must be securely fixed to prevent displacement-induced short circuits or poor contacts.
Sealing: Effective isolation from moisture and air to prevent cell oxidation and swelling.
Thermal management: Rapid heat dissipation via thermal conductive adhesives to maintain stable battery performance.
Traditional cell bonding relies on manual dispensing or semi-automated equipment, which present significant drawbacks. Manual dispensing is inefficient, with inconsistent adhesive volume and poor uniformity; semi-automated systems depend on fixed molds, making them inflexible for producing different cell models.
However, dispensing machines and potting machines enable automated production with high reliability, precision, and superior sealing.
(1) High-precision quantitative dispensing technology
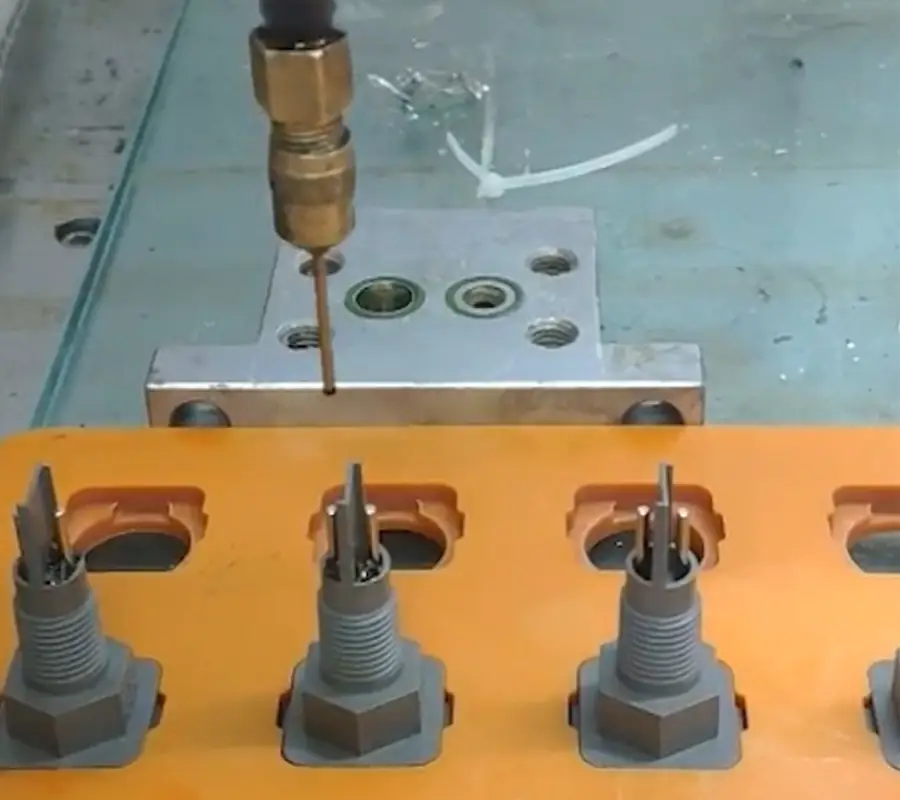
Automated dispensing machines equipped with high-precision metering pumps and pressure control systems enable accurate distribution of minute adhesive volumes. Taking screw-type dispensing pumps as an example, their minimum output reaches 0.01 microliters, with adhesive volume errors controlled within ±1%. This ensures uniform adhesive layers and consistent thickness in cell bonding. When bonding square lithium battery cells to their casings, the dispenser precisely applies adhesive lines just 1mm wide around the cell perimeter according to design specifications. This ensures optimal bonding strength while preventing adhesive overflow that could compromise battery performance.
(2) Multi-axis interlocking and vision positioning system
New energy battery cells feature complex structures, with dispensing paths often traversing irregular areas like curved surfaces and corners. The dispensing machine’s multi-axis interlocking robotic arm (e.g., 4-axis or 5-axis) enables flexible movement in three-dimensional space, precisely conforming to the cell’s contours. Simultaneously, the vision positioning system uses industrial cameras to capture the cell’s real-time position and orientation, automatically correcting deviations in the dispensing path. During cylindrical lithium battery cell assembly bonding, the dispensing machine utilizes vision positioning technology to rapidly identify cell orientation angles, ensuring bonding positional accuracy within 0.05mm for each cell.
(3) Intelligent process parameter control
The dispensing machine automatically optimizes parameters based on adhesive properties and cell materials. For instance, when adhesive viscosity fluctuates with ambient temperature, the system adjusts dispensing pressure and speed to maintain consistent adhesive volume. Sensors continuously monitor pressure and flow data during dispensing, triggering immediate alarms and shutdowns upon anomalies to prevent defective products. After implementing intelligent dispensing machines, a battery factory reduced cell bonding defect rates from 3% to 0.5% while boosting production efficiency by 40%.
(4) Adaptation and mixing technology for novel adhesives
New energy batteries demand adhesives with stringent performance requirements, including high bonding strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and flame retardancy. Dispensing machines can accommodate various novel adhesives such as thermal conductive silicone and epoxy resins. For two-component adhesives, dispensing machines feature high-precision dynamic mixing devices to ensure precise blending ratios of A and B components, maximizing adhesive performance. In soft-pack lithium battery tab bonding, using two-component thermal conductive adhesives with dispensing machine mixing technology enhances thermal conductivity between tabs and cells by 30%, effectively lowering battery operating temperatures.
b.Power battery shell sealing – potting machine
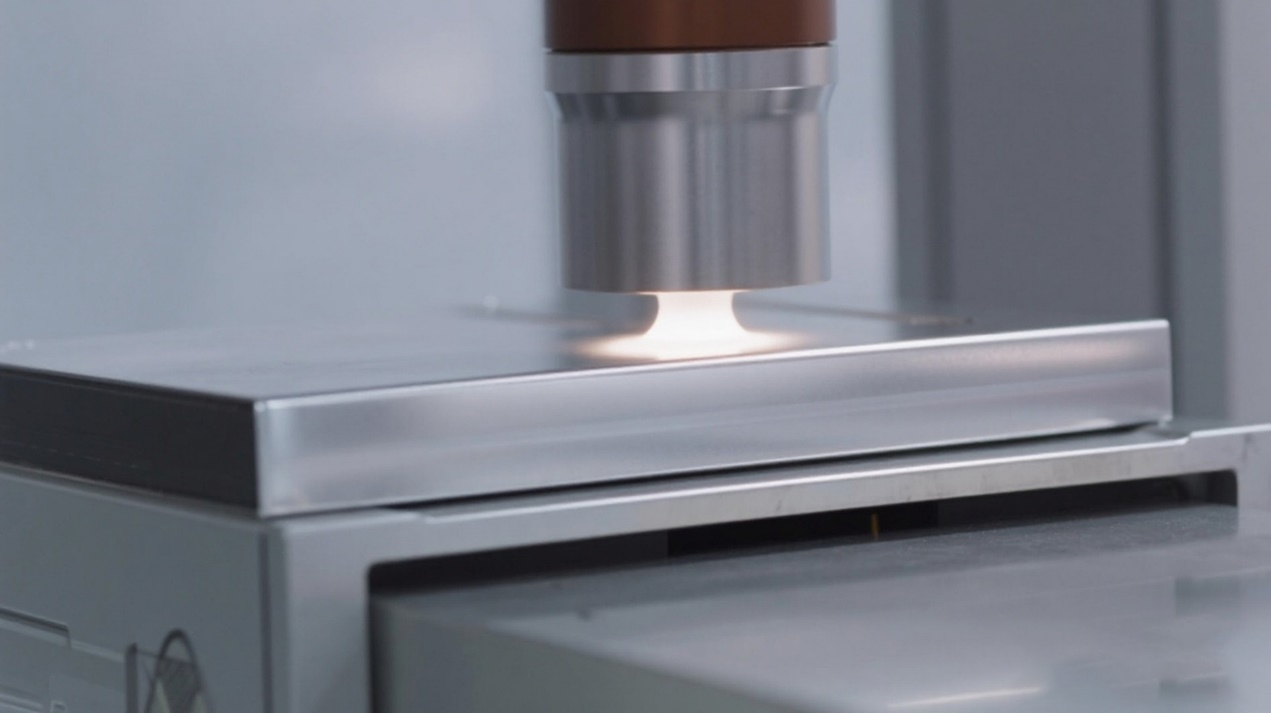
Power battery shell sealing requires a battery potting machine. By injecting sealant, moisture, dust, and other contaminants are effectively prevented from entering the battery interior, avoiding internal short circuits and other faults. This enhances the protection rating of power batteries, meeting the operational requirements of electric vehicles in various harsh environments.
Taking the sealing of a power battery’s top cover as an example, polyurethane or silicone material must be uniformly applied to the metal-plastic joint surface with positioning accuracy of ±0.02mm. The adhesive layer thickness must be controlled within 0.1-0.3mm. This precision dispensing effectively prevents electrolyte leakage while withstanding mechanical stress from vehicle vibrations.
 c.Battery pack encapsulation – adhesive dispensing machine
c.Battery pack encapsulation – adhesive dispensing machine
During battery module assembly, potting machines inject structural adhesives into connection points, providing reliable mechanical bonding strength. These adhesives must not only exhibit excellent adhesion but also withstand external forces like vibration and impact during vehicle operation. This ensures stable module connections in harsh environments, safeguarding electric vehicle safety.
Encapsulation and protection: vacuum potting system technology is employed to encapsulate the battery pack interior, filling voids and securing internal components while providing shock absorption, moisture resistance, and insulation protection.
![]()
d.Thermal silicone coating between power battery modules —– dispensing Machine + dual-component screw valve
Sealant is applied at the junctions between cells and module housings to form a waterproof and dustproof barrier (e.g., IP67 rating). This prevents electrolyte leakage and external contaminant ingress, ensuring battery reliability in harsh environments.
Thermal compound filling: intelligent dispensing machines apply thermal silicone gel (thermal conductivity >5W/m·K) between battery modules. Dual-component screw valves precisely control mixing ratios (1:1 to 32:1) with bead width tolerance ≤0.1mm, boosting heat dissipation efficiency by over 30%.
Sealing & Leak Prevention: vacuum injection technology eliminates air bubbles, ensuring battery casing achieves IP67 sealing standards. Compatible with CTP/CTC module-free designs.
e.Supporting functionality
Thermal Optimization: Thermal paste application improves heat transfer efficiency between battery components, helping regulate temperature, prevent overheating, and enhance battery performance and lifespan.
Noise reduction & vibration Damping: Utilizing materials like foamed silicone in battery modules through dispensing reduces vibration and noise, enhancing system stability.
Looking ahead, as the new energy sector continues to evolve, dispensing and potting machines will see increasingly widespread and sophisticated applications. Concurrently, driven by technological advancements and intelligent systems, these machines will advance toward greater automation and intelligence, providing robust support for the new energy industry’s growth.