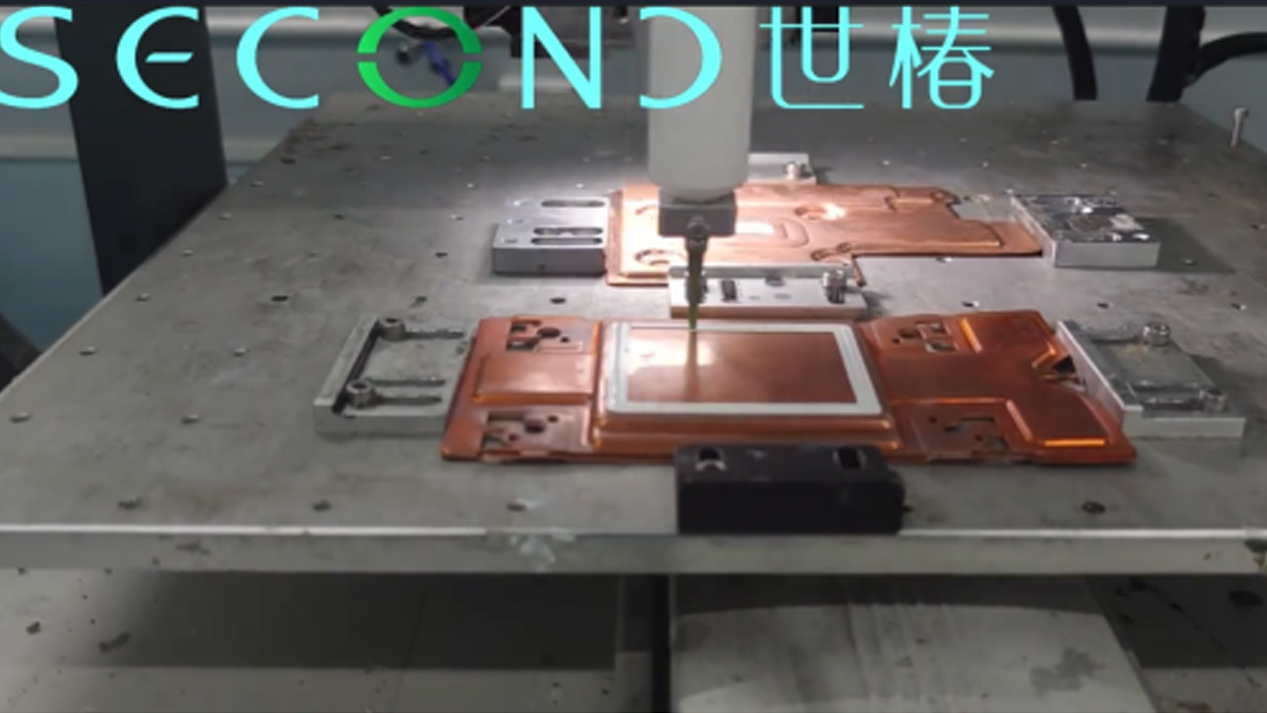
Precision dispensing of thermal conductive gel for high-performance computer CPU/GPU cooling modules?
Case Study on Thermal Gel Dispensing in Computer Heat Sinks: Background, Challenges, Solutions, Process Key Points, and Benefit Analysis.
1.Project Background
With the continuous increase in the power consumption of computer CPUs and GPUs (especially gaming laptops, high-end desktops, and servers), heat dissipation has become crucial in determining performance stability and lifespan. In traditional heat dissipation solutions, in addition to the thermal grease on the core components, a large number of surrounding heat-generating components such as capacitors, MOSFETs, and memory chips need to be effectively cooled.
These components vary in height and spacing, and are sensitive to stress. Traditional thermal pads (gap pads) suffer from uneven contact, limited thickness selection, and low efficiency of manual placement when dealing with complex, multi-height coplanar heat dissipation. Therefore, the industry is shifting towards solutions using thermal gel combined with automated dispensing technology.
Floor-standing precision dispensing equipment+ syringe dispensing
Ⅱ.Technical Challenges
1.High Filling Accuracy Requirements: Component gaps range from 0.1mm to 3mm, requiring complete filling without air bubbles, while preventing excessive overflow that could contaminate solder joints or gold fingers.
2.Material Characteristic Challenges: Thermal conductive gels are typically paste-like with strong thixotropic properties. Stable dispensing must be maintained during the dispensing process, and dispensing must be stopped immediately upon stopping, without stringing or dripping.
3.Process Stability: The dispensing path, volume, and height must be completely consistent to ensure uniform heat dissipation performance for each motherboard.
4.Production Efficiency: The dispensing must match the pace of a high-speed production line; dispensing and curing times must not become bottlenecks.
5.Reliability: After curing, the gel must withstand thermal cycling and vibration tests without cracking, peeling, or performance degradation.
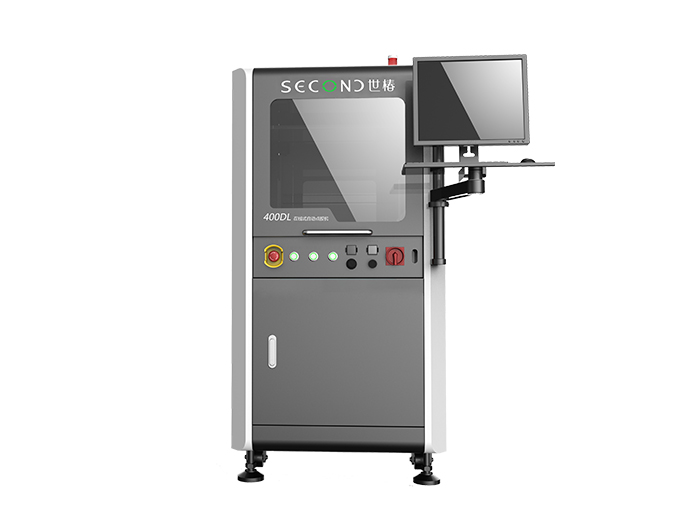
Automatic In-line PCB Glue Dispensing Machine SEC-DH400L
Second Intelligent In-line Automated Glue Dispensing Machine SEC-DH400L adopts an integrated mineral casting design, with ultra-high precision and super stability, powerful expansion capabilities, and can realize ion cleaning, dispensing, detection, UV exposure and other functions;
Adopting a gantry structure, it can bear large loads, stable structure, and a powerful CCD visual positioning system, which can meet the requirements of Mark point positioning, edge positioning, and 3D scanning positioning; strong scalability, and can expand AOI detection 3D detection, UV exposure curing and other functions;
Strong platform compatibility, contact and non-contact dispensing, single-head and multi-head synchronous dispensing, automatic compensation and adjustment of double-head spacing, five-axis dispensing function based on needle A/R displacement, etc.
III. Solution
1.Material Selection:
● Use a single-component silicone-based thermally conductive gel that can cure at room temperature or with heat.
● Key parameters: Thermal conductivity 1.5-3.0 W/m·K, viscosity range approximately 50,000 – 200,000 cP (selected according to specific process), low exudation, UL94 V-0 flame retardant rating.
2.Equipment Configuration:
Dispensing Platform: High-precision three-axis robotic dispensing system, repeatability ±0.02mm.
Dispensing Valve: Screw valve is preferred. Its precise metering, ability to handle high-viscosity fluids, and good linear control make it ideal for the continuous and stable dispensing of thermally conductive gel.
Vision System (Optional but Recommended): Used to locate the dispensing area on the PCB and compensate for incoming material deviations.
Pressure Tank: Works with the screw valve to provide stable supply pressure for high-viscosity gels.
3.Process Design:
● Path Planning: Employs a “U” or “spiral” dispensing path to cover the surface of the heating element, ensuring that the edges are also filled.
● Height Following: The Z-axis features pressure sensing or laser height following to ensure a constant distance between the dispensing head and the PCB surface, even if the PCB is warped.
● Needle Selection: Uses large-diameter tapered needles (e.g., 14G-18G) to reduce flow resistance and adhesion to the inner wall.
● Process Control: Precisely controls screw speed, dispensing time, and backflow parameters to completely eliminate stringing and dripping issues.
SMT automatic glue dispenser SEC-DH600L
Second Intelligent high precision smt automatic glue dispenser machine apply epoxy resin to the bottom of the PCB board for underfill
Second Intelligent smt automatic glue dispenser automation SEC-DH600L has the following advantages:
● CCD visual programming precise positioning, visual correction, improve programming efficiency and dispensing accuracy;
● Chinese and English operating system, the software interface layout is clear, the operation is simple, easy to learn and understand;
● Support visual inspection, integrated control of dispensing and visual inspection, multi-purpose machine, effective control of dispensing yield;
● It can be equipped with a lin e laser scanner for 3D path guidance and flexible dispensing;
● The software can support a variety of dispensing systems and functional module applications, such as automatic needle alignment, automatic
height measurement, dispensing weighing compensation, five-axis linkage and other functions, which can effectively overcome the difficulties of
various dispensing processes and help improve quality;
IV.Key Process Steps
1.Pre-treatment: Clean and preheat the PCB board (optional, reduces viscosity for better filling).
2.Programming and Teaching: Precisely set the 3D contour and path of each dispensing area in offline or online software.
3.Dispensing Execution:
● The screw valve rotates at a constant speed, dispensing the gel.
● The robot moves along the preset 3D path, precisely filling the uneven gaps between components with the gel.
● Using a method of dispensing before pressing or dispensing while pressing (using the weight of the heatsink or slight pressure), the gel automatically spreads and expels air.
4.Curing: Allow to stand at room temperature for 4-8 hours or accelerate curing by low-temperature heating (e.g., 80°C, 30 minutes).
5.Inspection: Use visual inspection or laser inspection to check the amount of adhesive, coverage area, and absence of contamination.
Ⅴ.Case Study Benefit Analysis
1.Performance Improvement:
Compared to air (thermal conductivity ~0.03 W/m·K), the gel completely fills the gaps, significantly reducing thermal resistance.
Contact thermal resistance is reduced by more than 30% compared to pre-cut gaskets, component temperatures drop by 5-15°C, and the system is more stable.
2.Cost Optimization:
Material Savings: Precise and controllable dispensing volume results in less waste compared to using standard thickness gaskets.
Labor Savings: Fully automated operation eliminates the need for manual gasket cutting, film removal, and mounting.
Simplified Inventory: One type of gel can replace multiple thermal pads of different thicknesses and shapes, simplifying BOM management.
3.Production and Reliability:
High Consistency: Machine dispensing eliminates the misalignment and air bubbles that can occur with manual gasket application.
High Adaptability: Easily handles design changes; only program modifications are needed, without the need for new gasket molds.
Enhanced Reliability: After gel curing, it forms an elastomer with excellent vibration and impact resistance, eliminating the risk of hardening or pumping out during long-term use.
Ⅵ.Key Success Factors
● Material and Process Matching: Optimal dispensing parameters must be adjusted based on the gel’s rheological properties (viscosity, thixotropic index).
● The “Pressure + Screw” Golden Combination: This is the industry consensus for consistently dispensing high-viscosity gels.
● Synergy with Heat Dissipation Module Assembly: The dispensing volume needs to be precisely calculated to match the final filling state after the heat sink is pressed down.
VII. Future Trends
Higher Thermal Conductivity: Higher requirements are placed on gel materials, moving towards 5W/m·K and above.
More Integration: The dispensing station is integrated with visual inspection, curing oven, and performance testing into a fully automated production line.
AI Process Optimization: Utilizing machine learning, the dispensing volume is automatically fine-tuned based on real-time temperature feedback to achieve “adaptive heat dissipation.”
In summary, the use of thermally conductive gel dispensing in computer heatsink applications is a prime example of the 3C electronics industry’s pursuit of high-performance, high-reliability, and highly automated manufacturing. It solves the design challenges of multi-height coplanar heat dissipation and, through precise fluid control technology, maximizes the efficiency and optimizes the cost of heat dissipation interface materials, becoming a standard process in the manufacturing of high-end computers, data center servers, and graphics cards.
Second Intelligent has played an important role in theresearch, development, manufacturing, pre-sales and after-sales services of fluid dispensing robot, potting and coating solutions which range from various types of automatic fluid dispensing, potting, two-component potting machines and coating machines with desktop, free-standing, inline or cobot combined systems, and widely used in global electrical, electronics, home appliances, automobile, telecom, pharmaceutical, automotive electronics, semiconductor, aerospace, LED and more.