Application of dispensing machines in the electrical control system of new energy vehicles
Dispensing and potting machines are primarily employed in the manufacturing of new energy vehicles within the three-electric systems ( power batteries, drive motors, and electronic control systems ). Through high precision, automation, and intelligent control, they fulfil the industry requirements for new energy vehicle production.
1.What are the “Three Electrics”in New Energy Vehicles?
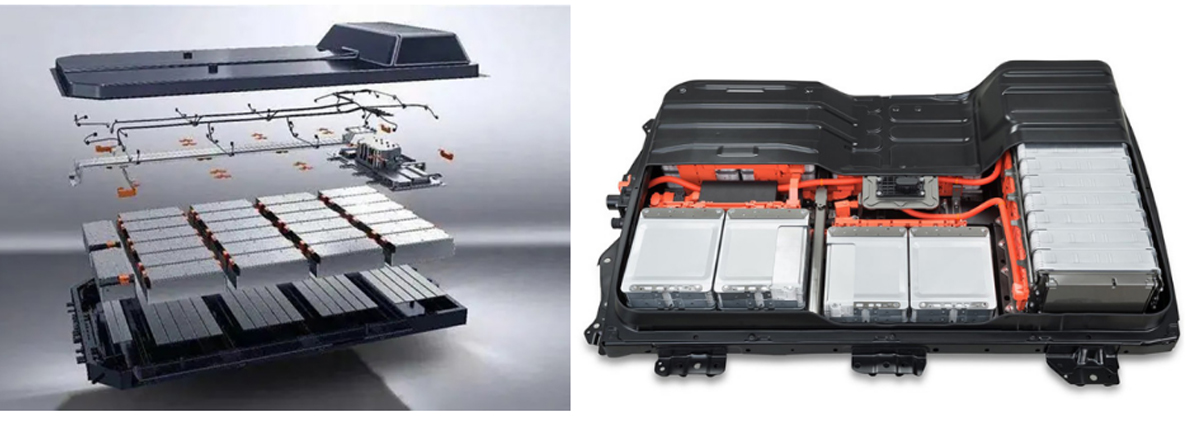
( 1 ) Battery system Equivalent to the engine in a petrol vehicle, it serves as the power source. Functioning as an energy storage device, it stores direct current (DC) electricity. This is essential because, unlike trams that operate on overhead lines, vehicles cannot be continuously powered by an external source during operation.
( 2 ) Electric drive system This functions as the equivalent of a petrol vehicle’s gearbox. The battery supplies power to the motor via the motor controller, and the motor’s rotation propels the vehicle forward. Modern automotive motors predominantly utilise permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), a type of AC motor. These offer high power output, light weight, compact size, and a wide rotational speed range, making them widely adopted.
( 3 ) Electronic control system Also termed the intelligent power module, this constitutes the core control unit of an electric vehicle. It directly collects acceleration/deceleration signals, braking signals, and gear position signals via hardwired connections. Through the CAN bus, it gathers battery status information, interprets driver intent, and regulates the drive motor’s operation based on the vehicle’s state to ensure normal driving. Both forward and reverse rotation of the motor are controlled by the motor controller, which also safeguards the motor.
二、Application of dispensing machines in the electronic control industry
(1)CIPG/FIPG dispensing process for electronic control systems (sealing dispensing)
Process description:
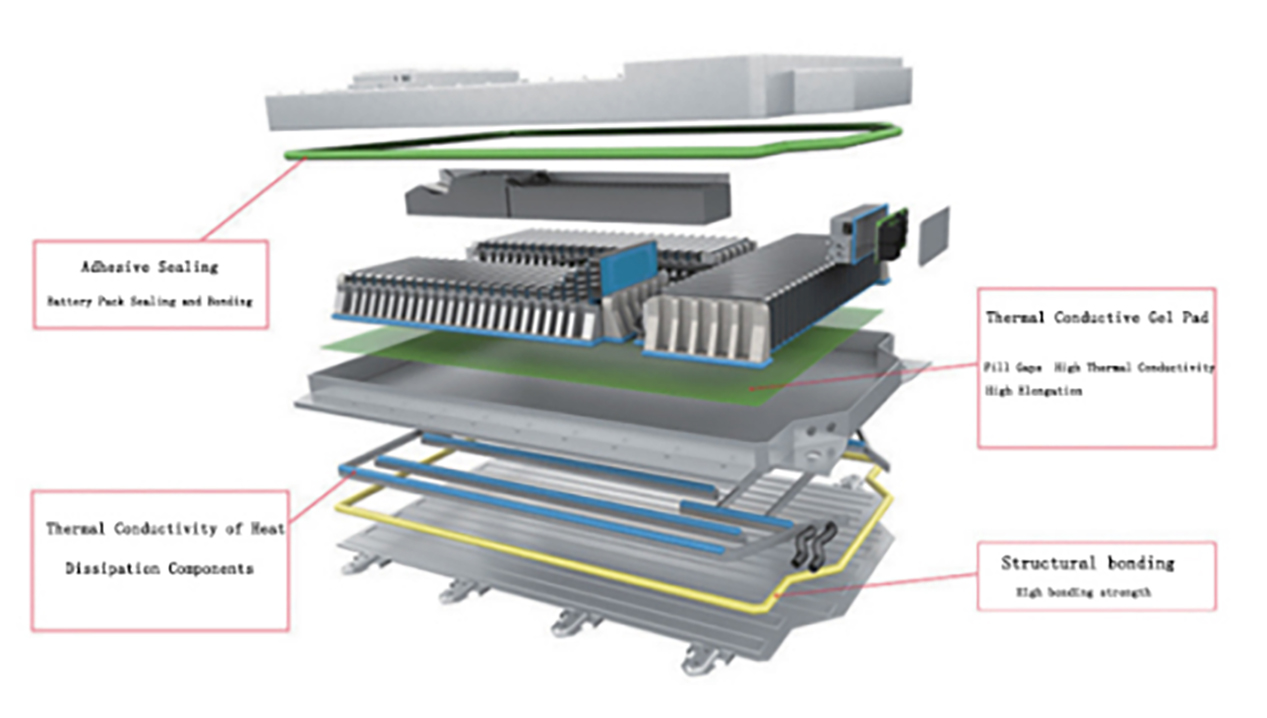
‘Sealing’ denotes a continuous adhesive bond. Within new energy vehicle powertrain manufacturing, sealants are typically employed as FIPG (Form-In-Place Gasket) and CIPG (Cure-In-Place Gasket). The adhesive forms a continuous liquid seal between the housing and cover plate, preventing ingress of dust, moisture, and other contaminants that could damage sensitive components or electronic elements. Key application points include the end caps of electric vehicle motors, BMS, OBC, screens, and other automotive electronic enclosures.
CIPG characteristics:
Sealing achieved through compression;
Sealed components remain disassemblable;
Automation replaces manual labour for precise dispensing and assembly;
Clamping force adjustable to specifications.
FIPG Characteristics: Achieves sealing through adhesion; simplified process reduces production costs; suitable for diverse structural components; mitigates risks of localised excessive stress.
FIPG characteristics:
Achieves sealing through adhesion; simplified process reduces production costs; suitable for diverse structural components; mitigates risks of localised excessive stress.
Applications:
Sealing and bonding processes for vehicle-mounted BOC, DC/DC, CCU, EVCC, PTC, and MBS controller housings.
Adhesives used:
Single/dual-component silicone sealants, polyurethane sealants.
CIPG/FIPG dispensing solutions
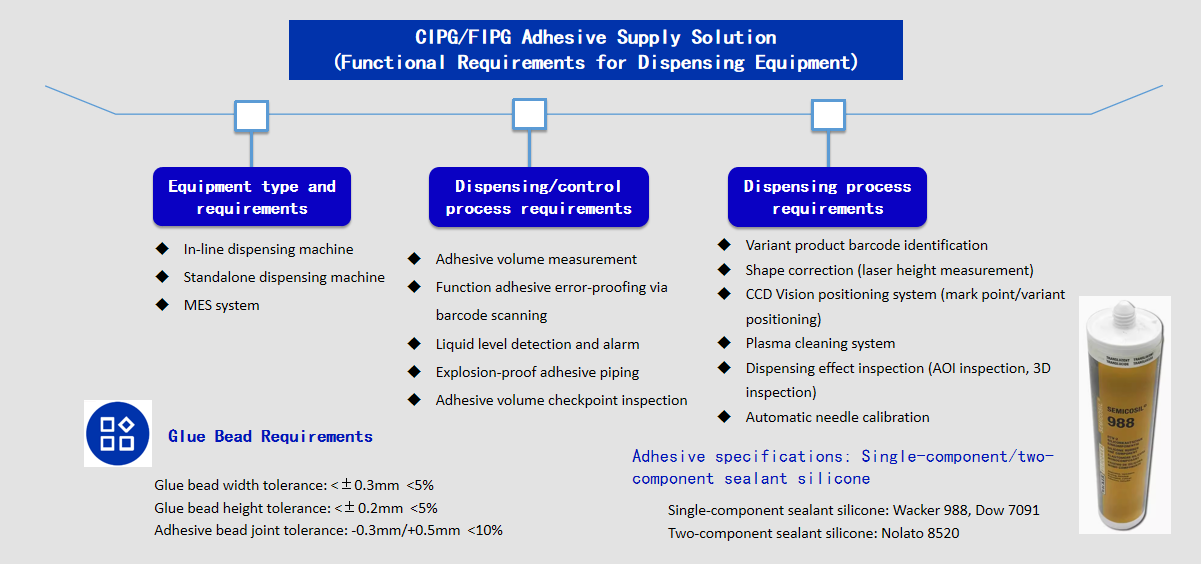
1.CIPG/FIPG dispensing equipment functional requirements
Adhesive specifications: Single-component/two-component silicone sealants
Single-component silicone sealants: Wacker 988, Dow Corning 7091
Two-component silicone sealants: Nolato 8520
B.Glue bead requirements:
Glue bead width tolerance: <±0.3mm Less than 5%
Glue bead Height requirement: <±0.2mm Less than 5%
Glue bead Joint requirement: -0.3mm/+0.5mm Less than 10%
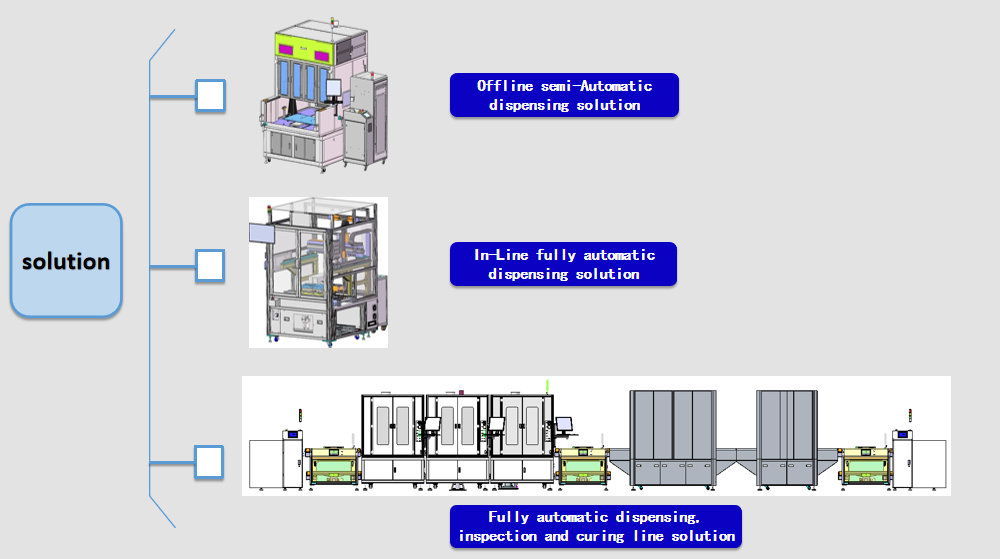
C.Solutions
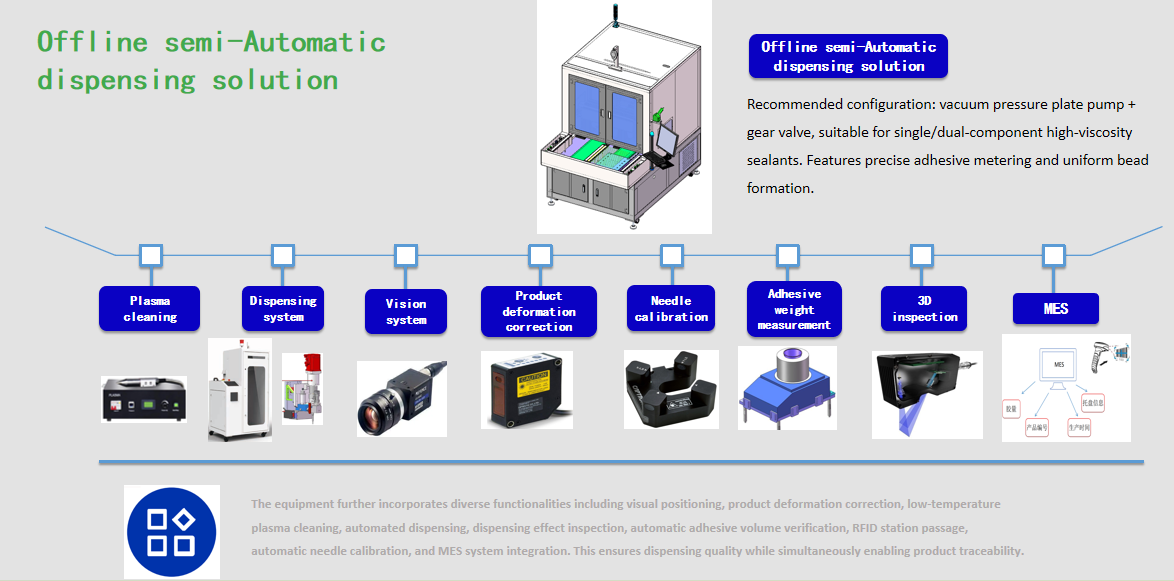
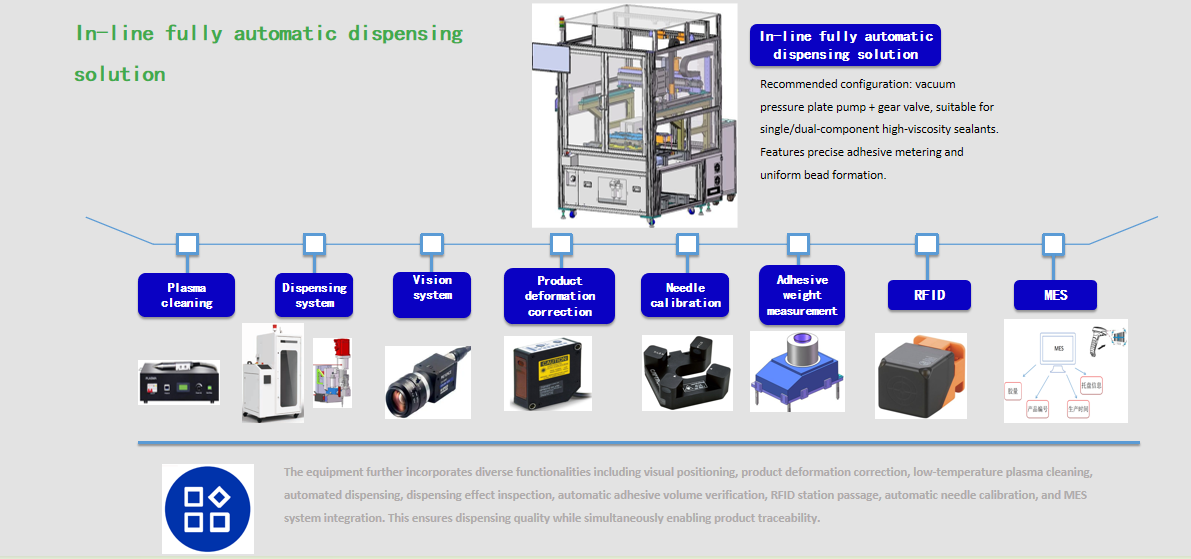
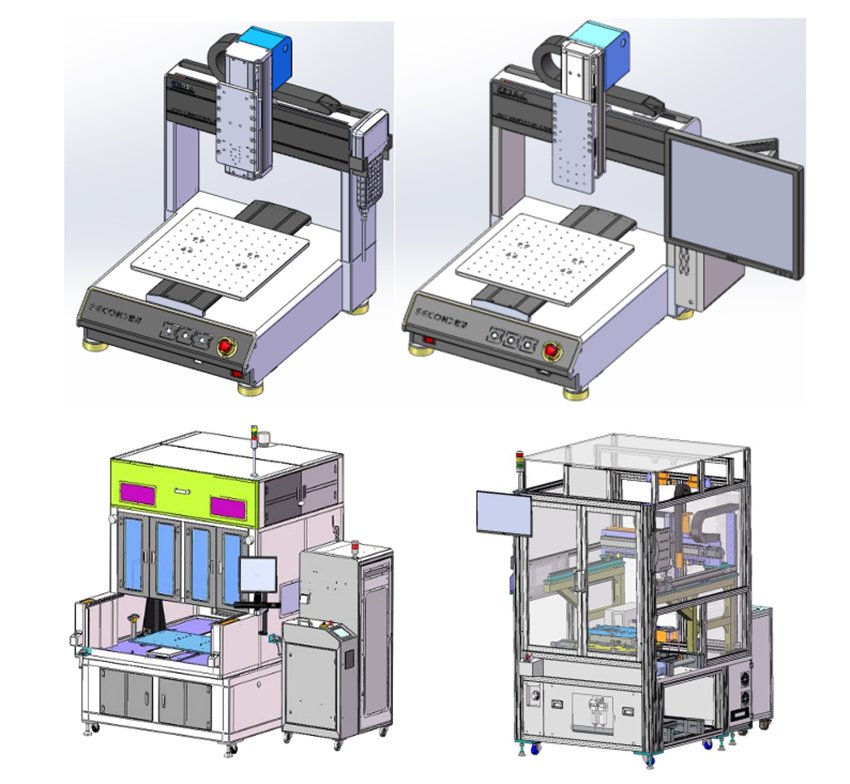
Offline semi-automatic dispensing machine solution
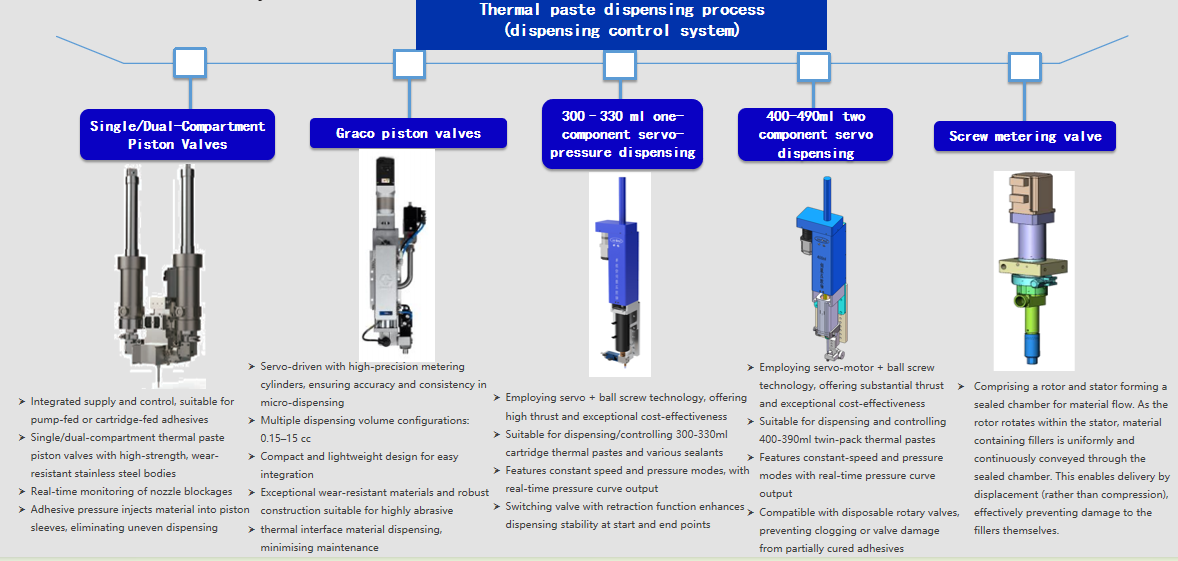
Recommended configuration: Vacuum pressure plate pump + gear valve. Suitable for single/dual-component high-viscosity sealants, offering precise volume control and uniform bead formation.
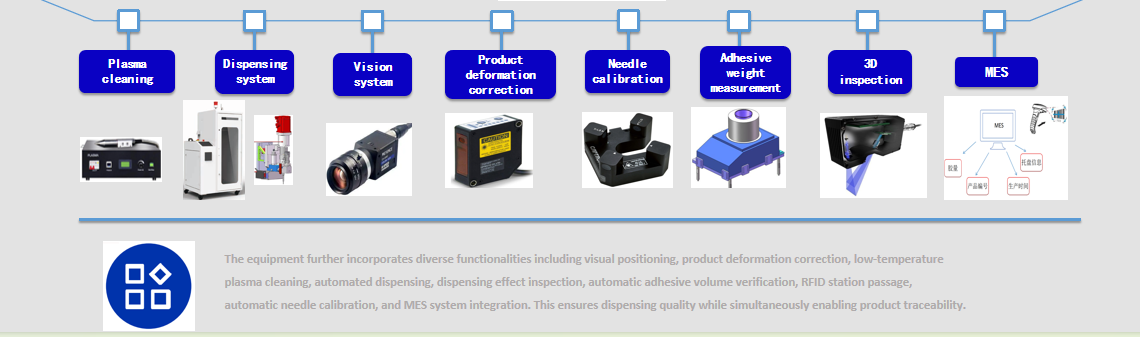
The equipment also incorporates extensive functionalities including vision-based positioning, product deformation correction, low-temperature plasma cleaning, automated dispensing, dispensing effect inspection, automatic adhesive volume verification, RFID station passing, automatic needle calibration, and MES system integration. This ensures dispensing quality while enabling product traceability.
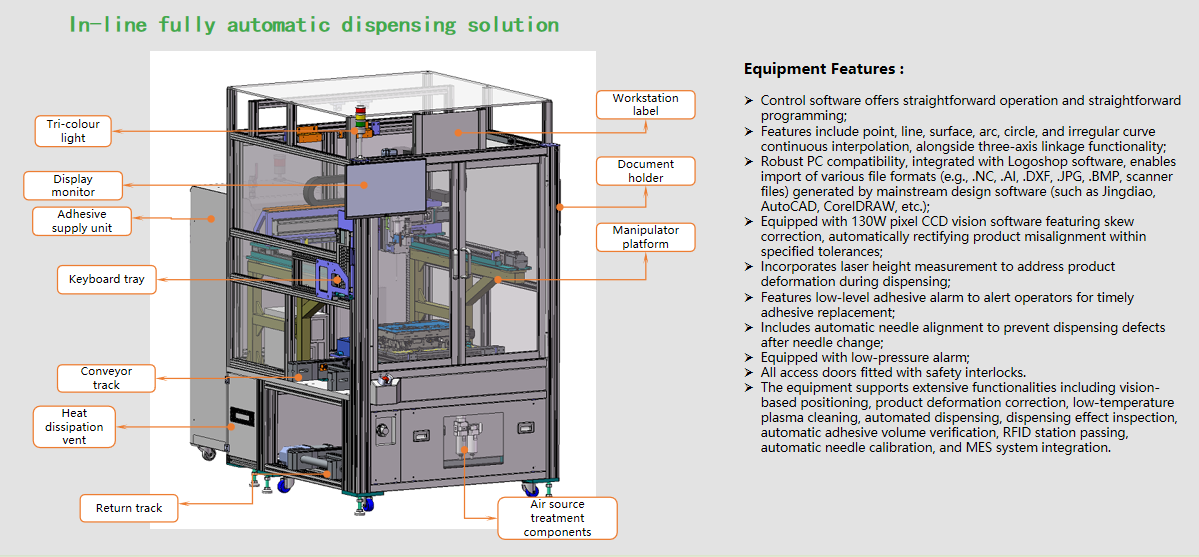
In-line fully automatic dispensing machine
Recommended configuration: vacuum pressure disc pump + gear valve. Suitable for single/dual-component high-viscosity sealants, offering precise adhesive volume control and uniform bead formation.
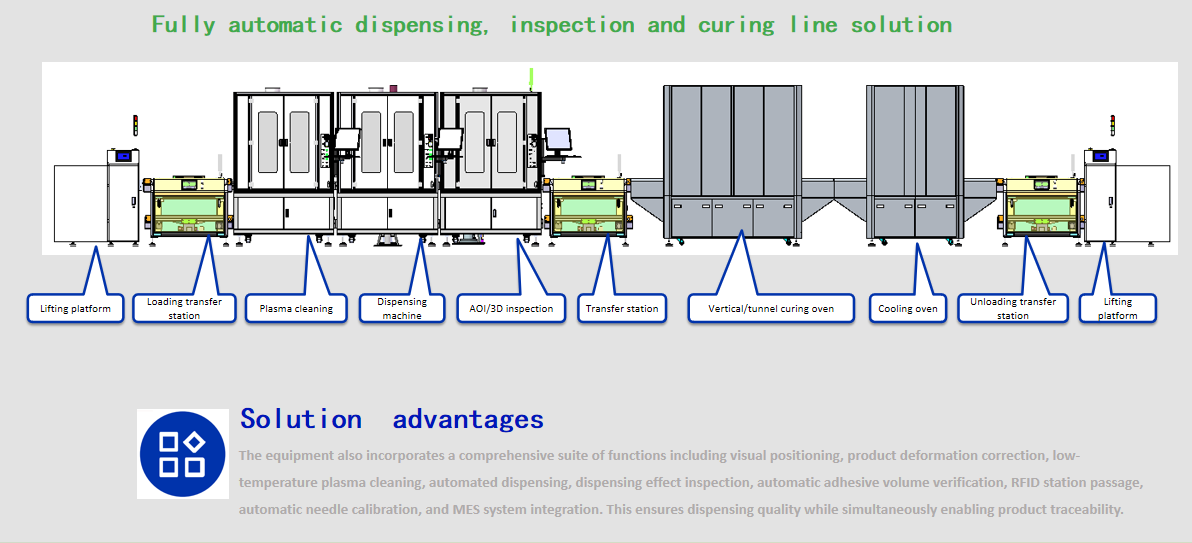
Fully automatic dispensing, inspection & curing line solution
The equipment also incorporates a comprehensive suite of functions including visual positioning, product deformation correction, low-temperature plasma cleaning, automated dispensing, dispensing effect inspection, automatic adhesive volume verification, RFID station passage, automatic needle calibration, and MES system integration. This ensures dispensing quality while simultaneously enabling product traceability.
(2)Thermal compound dispensing process for power devices ( hotspot dispensing)
Purpose: Suitable for thermal interface applications between internal power devices and heat sinks/enclosures in automotive BOC, DC/DC converters, CCUs, EVCCs, PTCs, and MBS controllers.
Adhesive: Thermal grease ( silicone grease )
Application : Primarily used for thermal conduction between battery cells and between cells and liquid cooling pipes. Application forms include gaskets, potting, and filling.
Characteristics:
- Complies with UL94 V-0, RoHS, PFOS, PFOA standards and HF requirements;
- High thermal conductivity (0.8-5 W/m·K);
- Shock-resistant, prevents mechanical damage, non-corrosive to substrates;
- Low molecular weight (D3-D10) siloxane content controllable below 300 ppm;
- Free from organotin compounds;
- Exceptional high and low temperature resistance, operating range from -55°C to 200°C;
- Excellent adhesion properties;
- Superior weather resistance, ozone resistance, and chemical resistance;
Thermal compound dispensing solutions
(1)Basic platform:desktop dispensing machines (stepper basic version, PC servo version), offline semi-automatic dispensing solutions, online fully automatic dispensing solutions .
(2) Expansion modules:
The equipment incorporates extensive functionalities including vision-based positioning, product deformation correction, low-temperature plasma cleaning, automated dispensing, dispensing effect inspection, automatic adhesive volume verification, RFID station passing, automatic needle calibration, and MES system integration. This ensures dispensing quality while enabling product traceability.
(3) Adhesive supply and control module (selectable based on customer packaging and adhesive viscosity)